As we approach 2025, non-invasive Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) are showing great promise in treating depression. These BCIs are a new kind of mental health technology. They aim to offer more personalized and effective care using the latest in neurotechnology.
Non-invasive BCIs for depression are gaining more attention in mental health. They allow for more targeted and efficient treatments. This could greatly improve mental health care by making treatments better and more enjoyable for patients.
Introduction to Non-Invasive BCIs for Depression
The field of non-invasive BCIs for depression is growing fast, with new treatments and technologies coming out. It’s important to keep up with these advancements for effective treatment. By looking into the newest non-invasive BCI therapies, we can see how they can change mental health care.
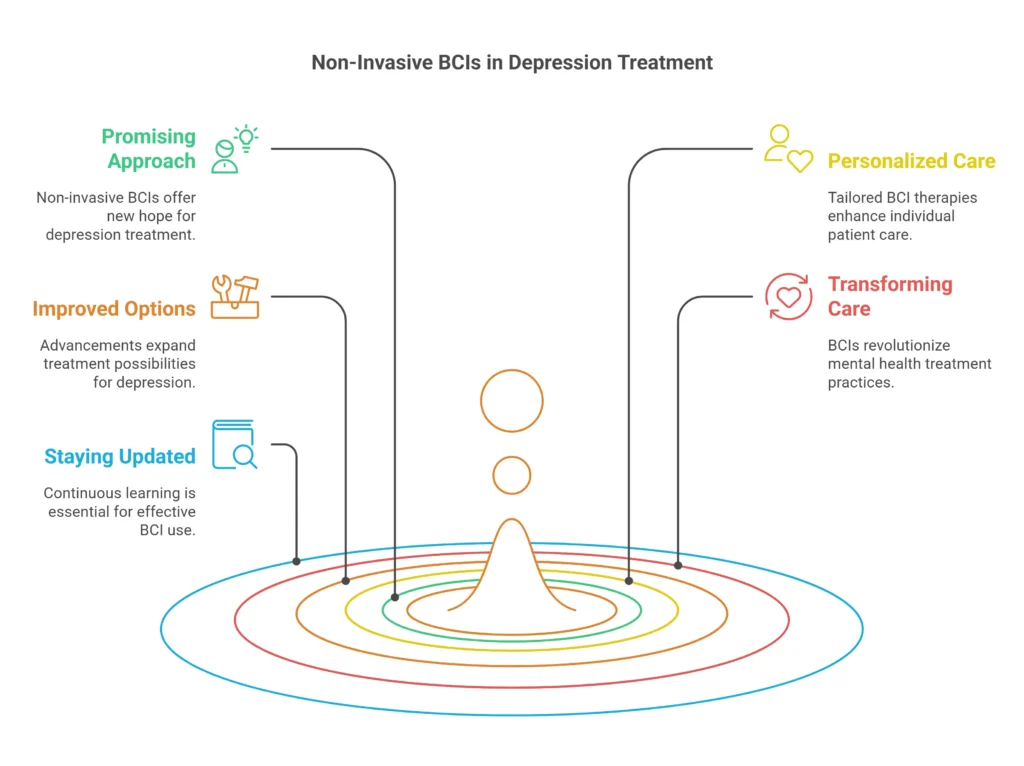
Key Takeaways
- Non-invasive BCIs offer a promising approach to depression treatment
- Non-invasive BCIs are a type of mental health technology that provides personalized care
- The latest developments in non-invasive BCIs are improving depression treatment options
- Non-invasive BCIs have the power to change mental health care
- Staying updated on the latest non-invasive BCI therapies is key for effective depression treatment
- Non-invasive BCIs are becoming more vital in mental health technology
Understanding Non-Invasive BCIs in Mental Health Treatment
Brain-computer interfaces, or BCIs, have changed mental health treatment. They let people control devices or talk to others with their brain signals. This is a new way to help with depression.
Non-invasive BCIs are getting more attention because they are safe and easy to use. They use neurofeedback to help people control their brain signals. This can help reduce depression symptoms. It’s a new option compared to old methods.
Some key benefits of non-invasive BCIs in mental health treatment include:
- Targeted symptom relief: BCIs can be made to focus on specific depression symptoms, like brain activity changes.
- Personalized treatment: Neurofeedback lets people help design their own treatment, fitting it to their needs.
- Non-invasive: Unlike invasive BCIs, non-invasive ones don’t need surgery. This lowers the risk of bad side effects.
As research keeps finding out more about non-invasive BCIs in mental health, it’s key to understand the tech and its uses. By looking into brain-computer interfaces and neurofeedback, we can find new ways to deal with depression and other mental health issues.
Non-Invasive BCIs for Depression: 2025’s Top Therapies and Applications
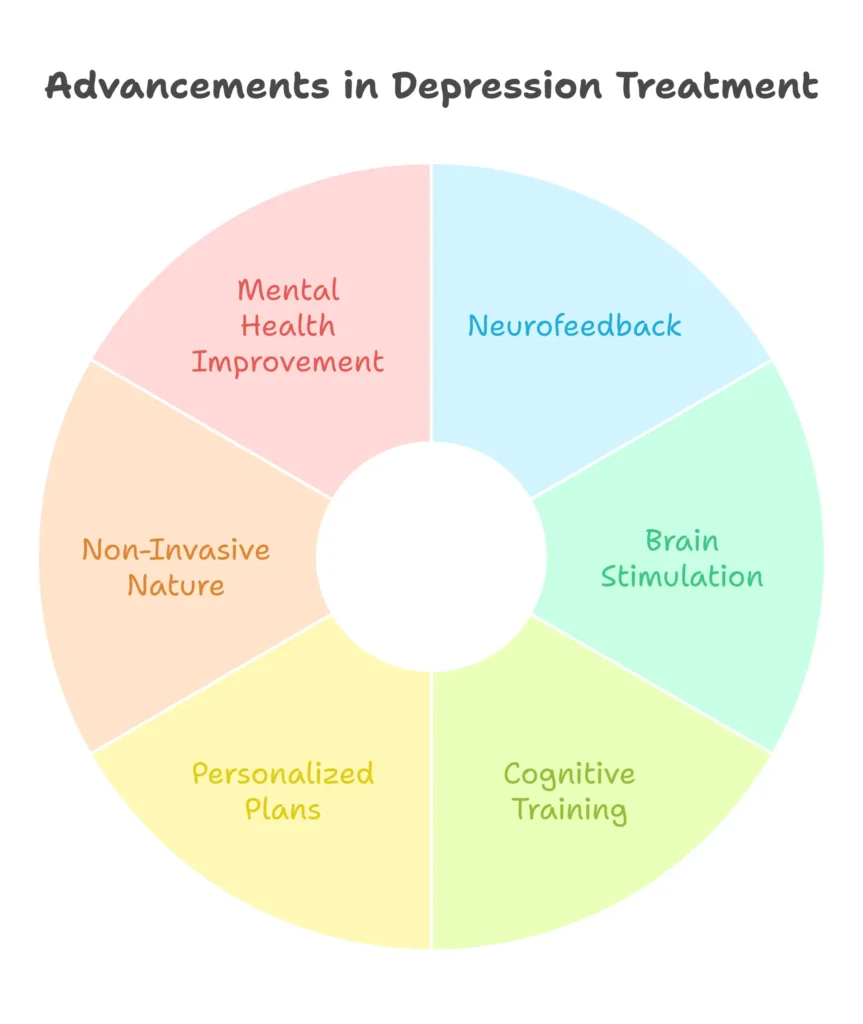
Non-invasive BCI therapies are changing how we treat depression. They are more personalized, effective, and easy to access than old methods. In 2025, the best treatments will use neurofeedback, brain stimulation, and cognitive training.
These new treatments are transforming depression care. They offer hope to those who didn’t get better with traditional methods. By looking into these therapies, we can see how non-invasive BCIs can boost mental health tech and help treat depression.
Non-invasive BCI therapies have many benefits:
- They offer personalized plans for each person.
- They are non-invasive and don’t hurt.
- They help improve thinking and feeling better.
- They make mental health tech better for treatment.
As research grows, we’ll see more new BCI therapies. They promise to make mental health care better and treat depression well. These therapies are a big step forward in mental health.
| Therapy | Description | Benefits |
| Neurofeedback | Training to self-regulate brain activity | Improved cognitive function, emotional regulation |
| Brain Stimulation | Non-invasive stimulation of brain areas | Enhanced mood, reduced symptoms |
| Cognitive Training | Targeted training to improve cognitive skills | Improved cognitive function, daily functioning |
Clinical Evidence and Treatment Outcomes
Looking into non-invasive BCIs for depression, we must check the clinical evidence and treatment results. Studies show promising results, with many patients seeing big improvements. These non-invasive methods add value to traditional treatments, with fewer side effects and more patient involvement.
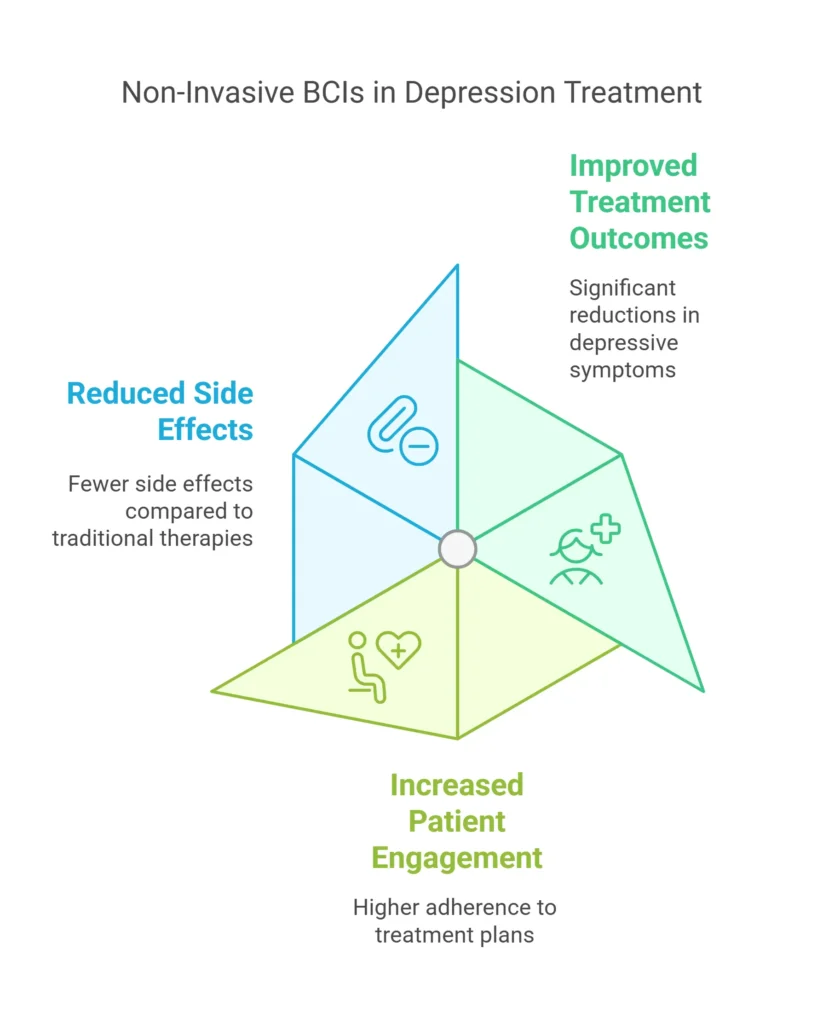
Clinical trials and studies have given us insights into non-invasive BCIs for depression. The evidence shows they can be a good treatment for those who didn’t get better with traditional methods. Some key findings are:
- Improved treatment outcomes: Non-invasive BCIs have been shown to improve treatment outcomes, with patients experiencing significant reductions in depressive symptoms.
- Increased patient engagement: Non-invasive therapies have been found to increase patient engagement, with patients more likely to adhere to treatment plans and attend follow-up appointments.
- Reduced side effects: Non-invasive BCIs have been found to have fewer side effects compared to traditional therapies, making them a more attractive treatment option for patients.
In summary, the clinical evidence and treatment outcomes show non-invasive BCIs are a valuable option for depression treatment. As research keeps growing, we’ll likely see more innovative uses of these therapies in treating depression.
Conclusion: The Future of Depression Treatment with Non-Invasive BCIs
Looking ahead, non-invasive brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) will be key in treating depression. These technologies are advancing fast, backed by solid clinical evidence. They promise to make mental health care more personalized, effective, and accessible.
Experts believe that using these advanced technologies will lead to better depression management. As non-invasive BCIs become more common, they could give patients a new way to find relief. This could mean better results, less stigma, and a more complete approach to treating depression.